In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the role of internal auditors is expanding beyond compliance to become a strategic driver of value creation through ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) assurance and sustainability integration. This blog explores the latest trends, challenges, and opportunities for internal auditors, drawing on insights from ERM CVS’s recent expert webinar. You can also download the webinar recording here.
1. ESG Assurance: Building Trust in a Changing Regulatory Environment
Organizations face growing demand for ESG assurance as stakeholders and regulators expect credible, transparent reporting. Internal auditors are uniquely positioned to drive ESG assurance, helping build trust and meet evolving regulations. The global trend toward mandatory sustainability disclosures is accelerating, with new standards emerging across regions, from the EU’s CSRD and Green Claims Directive to the U.S.’s state-specific GHG rules and Asia-Pacific’s ISSB-aligned requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- ESG assurance is now a strategic imperative, not just a compliance exercise.
- Internal auditors can help organizations navigate regulatory complexity and deliver credible, finance-grade sustainability data.
- Collaboration between IT, finance, and sustainability teams is essential for high-quality ESG reporting driven by a core need for accurate and consistent data.*1
2. Embedding Sustainability into Governance and Risk Frameworks
Internal auditors play a critical role in embedding sustainability into governance, risk, and performance frameworks. By aligning ESG with core business strategy and risk management, auditors enable organizations to move from reactive compliance to proactive value creation. Core elements of recommended climate related financial disclosures, according to TCFD 2017 remain fundamental to the ESG framework requirements and main areas of focus for internal audit.
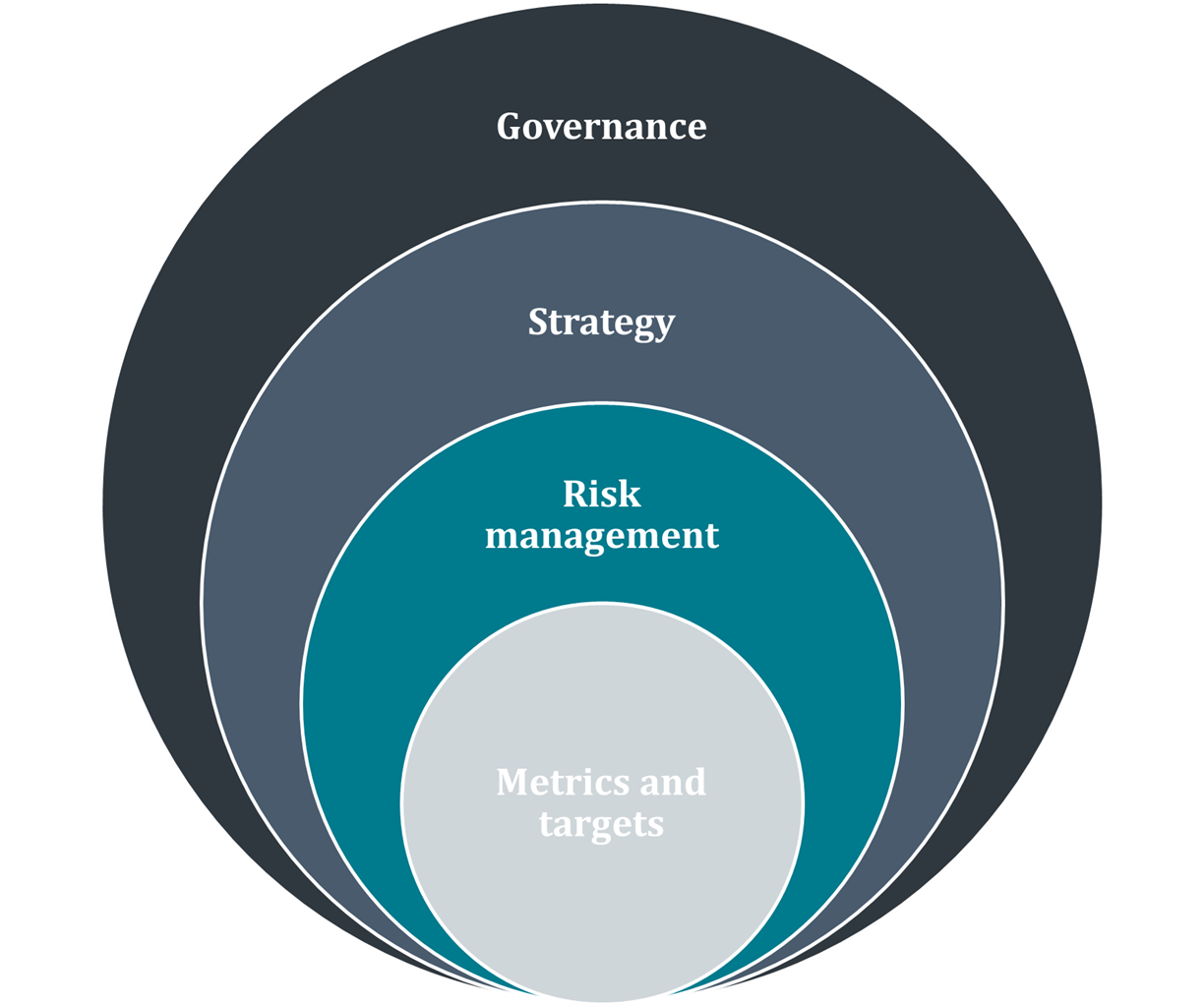
To strengthen ESG governance, organizations should integrate climate risks and opportunities into their governance structures, use scenario analysis to inform strategy and risk management, and ensure that metrics and targets for emissions and sustainability are robust and aligned with global frameworks such as TCFD, GRI, and SASB.Integrated ESG Audits: Efficiency and Holistic Assurance
Companies are increasingly favoring integrated audits that combine financial, sustainability, and regulatory assurance. This approach offers a holistic view, improves efficiency, and reduces duplication of effort.
3. Internal Auditor’s ESG Responsibilities:
- Improve ESG governance structures and control environments.
- Recommend relevant reporting metrics and assess adherence to regulations.
- Upskill senior management and boards in ESG.
- Conduct materiality and risk assessments on ESG reporting.
Sustainability is a journey, and organizations will find themselves at different stages of ESG reporting maturity.

Depending on your organizational state, additional internal audit support may be required until your teams are further developed, further information on internal auditing can be found here.
4. Determining what is important in creating your audit plan
The core of climate disclosures is outlined in the diagram below considering all factors of Environment (E), Social (S) and Governance (G). Aligning your goals and objectives so the right metrics can be evidenced is key.
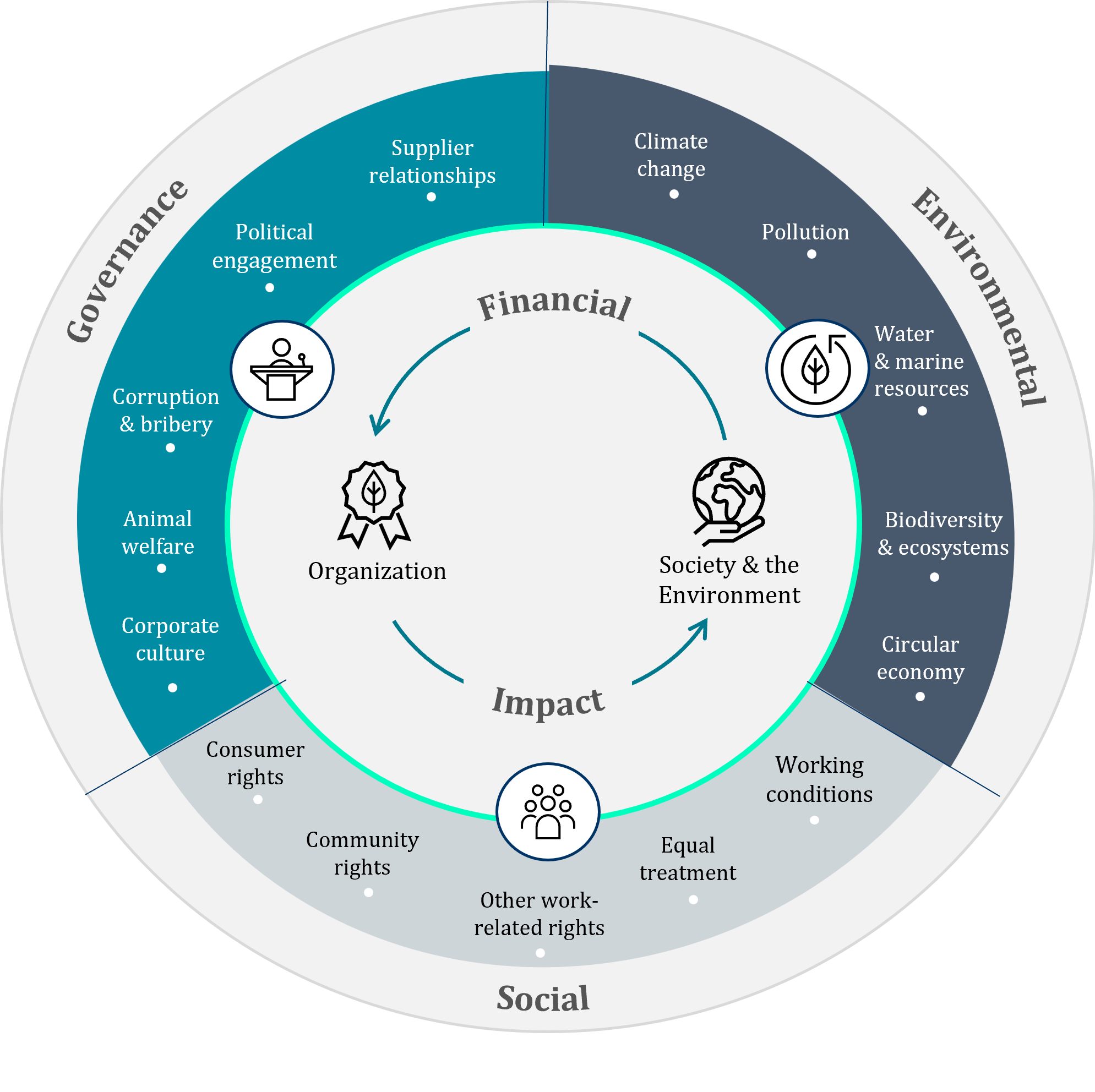
5. Strengthening ESG Reporting Across the Organization
Challenges persist in aligning ESG reporting across functions, particularly between sustainability teams, finance, and operational sites. Common issues include inconsistent data quality, limited resources, and communication gaps.
Opportunities for Improvement:
- Appoint an ESG Controller to oversee sustainability data governance.
- Define clear roles and responsibilities for ESG reporting.
- Develop practical guidance documents for data collection and validation.
- Establish robust audit trails and internal controls.
- Upskill teams to build ESG literacy and confidence.
- Engage Internal Audits to assess and validate effectiveness of sustainability related controls.
Find out more on ERM CVS assurance services here
6. Upskilling Internal Auditors for ESG: Competencies and Training
The shift from compliance to value creation requires internal auditors to develop new skills and competencies.
Core Skills for ESG Auditors:
ESG auditors require a blend of technical, interpersonal, and adaptive skills to deliver effective assurance in today’s evolving sustainability landscape:
- They need strong technical and analytical expertise, including ESG data literacy, regulatory intelligence, risk assessment across ESG domains, and digital competence with ESG software and analytics.
Part of the analytical skillset is around process improvement and problem solving, some useful training resources include 8 Disciplines Methodology for Problem Solving found here and Root Cause Analysis found here.
- Interpersonal and organizational transformation skills are essential, such as stakeholder engagement, change management, empathy, and ethical leadership.
- Professional and adaptive competencies are also critical, including continuous learning, strategic thinking, resilience, and agility.
Effective ESG auditor training relies on a combination of flexible, targeted approaches:
- Modular, integrated training programs help build proficiency across multiple standards.
- Standardized criteria are applied across regions, with programs adaptable to local needs.
- Continuous learning is linked to operational KPIs and business goals, ensuring ongoing relevance and impact.
Further information on ERM CVS ESG Internal Auditor training can be found here
7. Five-Year ESG Internal Audit Plan: Roadmap for Success
A structured, multi-year approach to ESG internal auditing helps organizations mature their assurance capabilities and deliver comprehensive value over time.
Year-by-Year Focus:
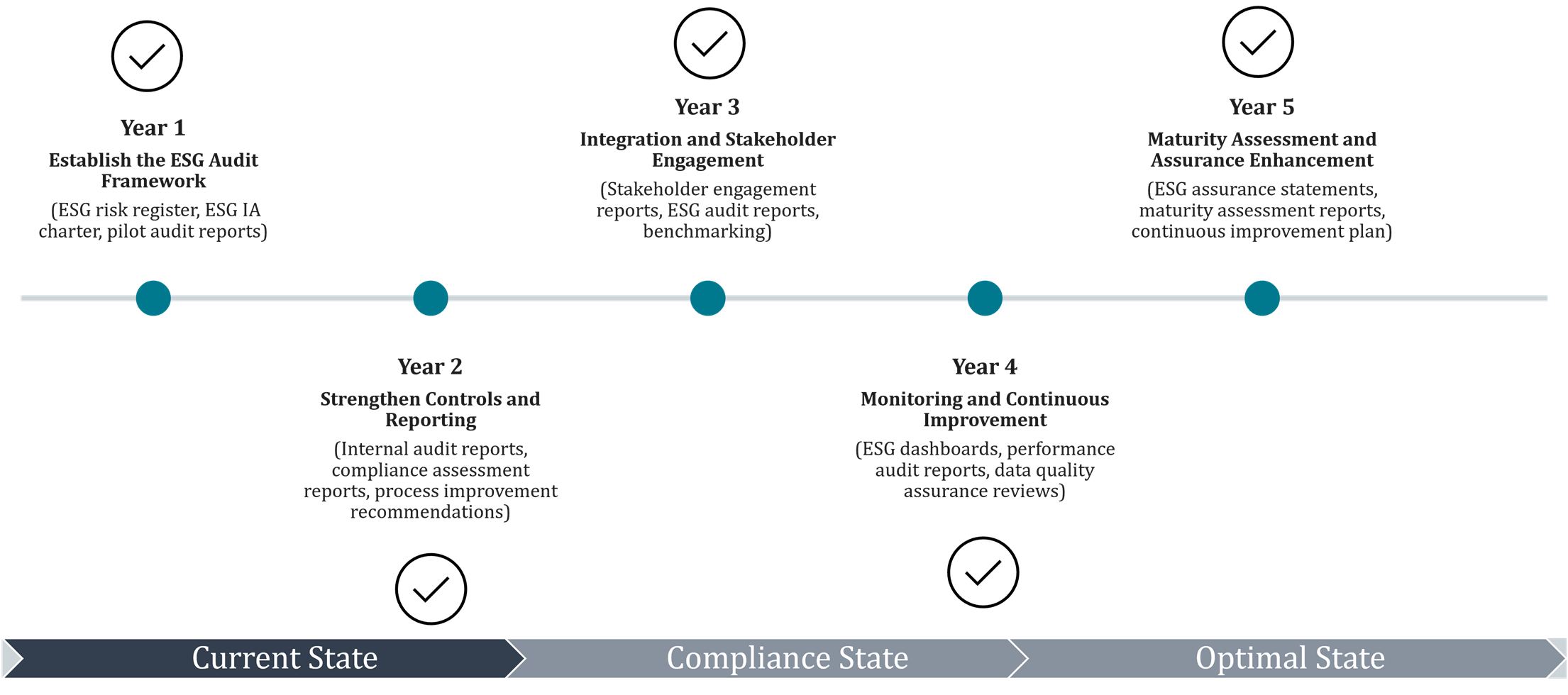
The ISSA 5000 standard is replacing ISAE 3000, with a greater emphasis on sustainability-specific knowledge and the use of subject matter experts, this is an important evolution for your third-party assurance providers who must adhere to ISSA 5000 from 2026 (exact timeline depends on jurisdiction).
Conclusion: The Journey from Compliance to Value Creation
Sustainability is a journey, and internal auditors are at the forefront of the shift from compliance to value creation in ESG and sustainability. By embracing integrated assurance, upskilling for new competencies, and fostering cross-functional collaboration, auditors can help organizations build trust, meet regulatory demands, and unlock long-term sustainable value.
For more insights, training opportunities, and resources, visit http://www.ermlearning.com or alternatively access our knowledge hub of previous webinar recordings and whitepapers here
Contact us here or email now post@ermcvs.com
*1 ERM 2025 Research - Sustainability Value Creation Partnership

 View all
View all 


